Legionnaires’ Disease in Lincoln, NH
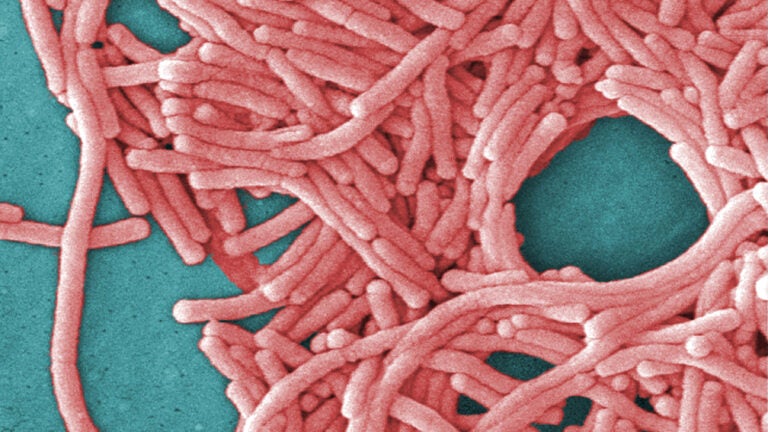
Legionnaires’ disease is a severe form of pneumonia caused by the bacterium *Legionella pneumophila*. This bacterium is commonly found in water sources, particularly in warm, stagnant water. While the disease is not contagious, it can be spread through the inhalation of contaminated water droplets, typically from sources like air conditioning systems, showers, and hot tubs. Symptoms of Legionnaires’ disease can include fever, chills, cough, muscle aches, and headache. In some cases, the disease can be fatal, especially for individuals with weakened immune systems.
History of Legionnaires’ Disease Outbreaks in Lincoln, NH, Lincoln nh legionnaires disease
While there have been no documented outbreaks of Legionnaires’ disease in Lincoln, NH, it is important to note that the disease can occur anywhere where *Legionella* bacteria are present. The state of New Hampshire has experienced several outbreaks of Legionnaires’ disease in recent years, particularly in areas with older infrastructure and water systems. These outbreaks highlight the importance of maintaining water systems to prevent the growth of *Legionella* bacteria.
Prevalence of Legionnaires’ Disease in Lincoln, NH
Data on the prevalence of Legionnaires’ disease in Lincoln, NH, is not readily available. However, the New Hampshire Department of Health and Human Services tracks cases of Legionnaires’ disease statewide. Based on statewide data, the prevalence of Legionnaires’ disease in New Hampshire is generally consistent with national averages. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that approximately 8,000 to 18,000 cases of Legionnaires’ disease occur in the United States each year.
Environmental Factors Contributing to Legionella Growth in Lincoln, NH
Several environmental factors can contribute to the presence of *Legionella* bacteria in Lincoln, NH. These include:
- Water temperature: *Legionella* bacteria thrive in warm water, particularly between 77°F and 108°F. Older water systems, particularly those with stagnant water, may be more susceptible to *Legionella* growth.
- Water stagnation: Stagnant water, such as in infrequently used pipes or showerheads, can provide an ideal breeding ground for *Legionella* bacteria.
- Water contamination: Contaminated water sources, such as those with high levels of organic matter, can also contribute to the growth of *Legionella* bacteria.
- Building infrastructure: Older buildings with aging plumbing systems may be more susceptible to *Legionella* growth due to corrosion and leaks.
Public Health Response and Prevention

The Lincoln, NH, health department plays a crucial role in safeguarding the community’s well-being, especially when it comes to potential health threats like Legionnaires’ disease. Their proactive approach includes monitoring cases, investigating potential sources, and implementing preventive measures to minimize the risk of outbreaks.
Identifying and Investigating Potential Sources of Legionella
The local health department employs a comprehensive strategy to identify and investigate potential sources of Legionella bacteria within the community. This involves:
- Surveillance and Case Reporting: The health department actively monitors reports of suspected Legionnaires’ disease cases. Prompt reporting by healthcare providers is essential for timely investigation and intervention.
- Environmental Sampling: Once a case is confirmed, the health department will collect environmental samples from potential sources, such as water systems in buildings, cooling towers, and decorative fountains. These samples are analyzed for the presence of Legionella bacteria.
- Site Inspections: Inspectors visit potential sources to assess their condition, identify potential risk factors, and recommend corrective actions. This includes evaluating water temperatures, plumbing systems, and maintenance practices.
- Epidemiological Investigations: The health department conducts thorough investigations to identify common exposures among cases, potentially linking them to a specific source. This involves interviewing patients, reviewing medical records, and gathering information about their activities and locations.
Preventing Legionnaires’ Disease Outbreaks
To mitigate the risk of Legionnaires’ disease outbreaks, the health department implements a range of preventive measures, including:
- Water Testing and Maintenance Protocols: The health department mandates regular water testing for Legionella bacteria in high-risk facilities, such as hospitals, nursing homes, hotels, and large buildings with complex plumbing systems. These facilities are also required to follow strict water maintenance protocols, including flushing water systems regularly, maintaining proper water temperatures, and keeping cooling towers clean and disinfected.
- Public Education and Awareness Campaigns: The health department conducts public education campaigns to inform residents about Legionnaires’ disease, its symptoms, and preventive measures. This includes distributing brochures, hosting community events, and utilizing local media to disseminate important information.
- Collaboration with Stakeholders: The health department works closely with local businesses, building owners, and property managers to ensure compliance with water safety regulations and to promote best practices for preventing Legionnaires’ disease. This collaborative approach fosters a shared responsibility for public health.
Impact on the Community: Lincoln Nh Legionnaires Disease
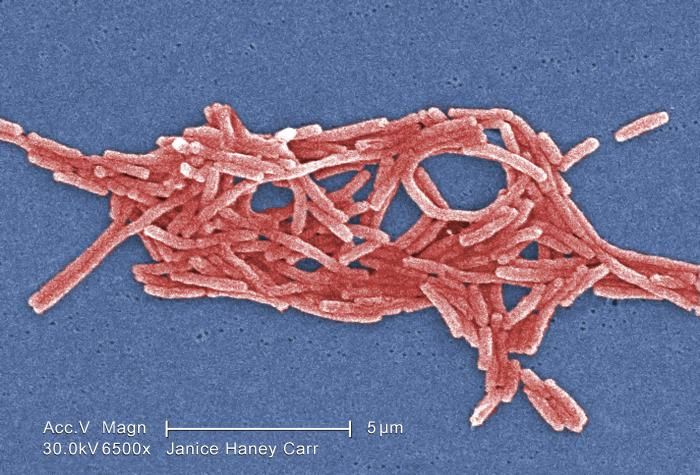
The outbreak of Legionnaires’ disease in Lincoln, NH, has had a significant impact on the health and well-being of residents, the local economy, and the community’s overall sense of security. The disease’s potential for serious illness and even death has caused widespread anxiety and fear, prompting a range of responses from residents, businesses, and local authorities.
Health and Well-being
The outbreak of Legionnaires’ disease has had a direct impact on the health and well-being of residents in Lincoln, NH. The disease, caused by a type of bacteria found in water sources, can lead to serious respiratory illness, including pneumonia. In severe cases, it can be fatal, particularly for individuals with underlying health conditions. The outbreak has caused a significant strain on the local healthcare system, with hospitals and clinics experiencing an influx of patients seeking diagnosis and treatment.
Economic Consequences
The outbreak has also had a significant impact on the local economy. Lincoln, NH, is a popular tourist destination, with a thriving hospitality industry. The news of a Legionnaires’ disease outbreak can deter visitors, leading to a decline in tourism revenue. Businesses, particularly those in the hospitality sector, have experienced a decrease in bookings and revenue, impacting their profitability and potentially leading to job losses. The outbreak’s economic impact is likely to be felt for some time, as it takes time to rebuild trust and confidence in the community’s safety.
Community Response
The community’s response to the Legionnaires’ disease outbreak has been multifaceted, marked by a mix of concern, resilience, and a strong sense of community. Residents have expressed concerns about the potential for further cases, the safety of public water sources, and the effectiveness of the public health response. However, the community has also come together to support those affected by the outbreak, offering assistance, information, and emotional support.
Lessons Learned
The Legionnaires’ disease outbreak in Lincoln, NH, has provided valuable lessons that can inform future prevention efforts. The outbreak highlights the importance of proactive measures to prevent the growth and spread of Legionella bacteria in water systems. These measures include regular testing and maintenance of water systems, particularly in public buildings and facilities, as well as public education campaigns to raise awareness about the disease and its prevention.
Lincoln nh legionnaires disease – The Lincoln, NH, Legionnaires’ disease outbreak serves as a stark reminder of the vulnerability of communities to unexpected health threats. It underscores the importance of being prepared, especially in areas like northeast Ohio , where potential emergencies can arise from a variety of sources.
The Lincoln outbreak highlights the need for swift action and robust public health systems to mitigate the impact of such events.
The outbreak of Legionnaires’ disease in Lincoln, New Hampshire, serves as a stark reminder of the invisible dangers lurking in our environment. Just as the complex history of tensions between Iran and Israel has shaped the geopolitical landscape of the Middle East, the outbreak in Lincoln has highlighted the need for vigilance and proactive measures to safeguard public health.
Understanding the root causes of such outbreaks, whether it be water systems or international conflicts, is crucial for building a safer future.
